Date: March 2018
Category: Artificial Intelligence, Machine Learning, Reinforcement Learning
Super Mario World playing agent.
Software
Python, Lua, Lsnes emulator, Zeromq
Project description
 The goal of this project is to create an agent that can successfully play Super Mario world for the SNES inside an emulator.
In 2013 Google’s deep mind published a paper describing how they created an agent that was able to successful replicate human level play in Atari 2600 games using a method called deep Q learning. Deep Q learning (DQN) is a technique that combines the reinforcement learning method of Q-learning with the power of a neural network. This project utilizes the same DQN algorithm albeit with a simplified neural network.
The goal of this project is to create an agent that can successfully play Super Mario world for the SNES inside an emulator.
In 2013 Google’s deep mind published a paper describing how they created an agent that was able to successful replicate human level play in Atari 2600 games using a method called deep Q learning. Deep Q learning (DQN) is a technique that combines the reinforcement learning method of Q-learning with the power of a neural network. This project utilizes the same DQN algorithm albeit with a simplified neural network.
The Deep Q network will receive the current state of the emulator. The state of the game consists of a screen capture of the play area. This image is then converted to an HSV color representation and resized to be an 88x88 image. The newly resized image is then ran through the convolutional neural network represented in figure 2.
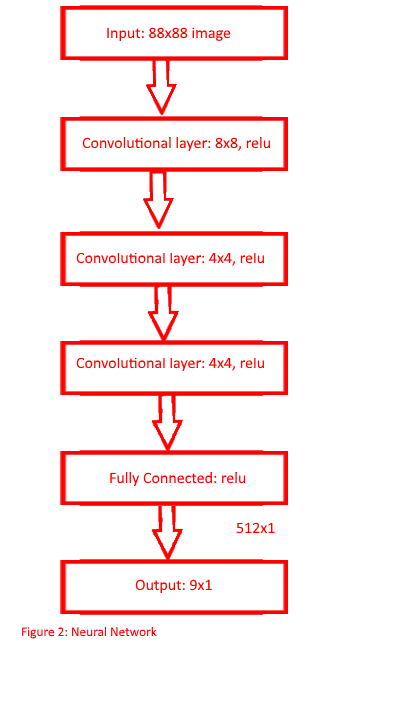
The neural network used in this project has the same setup as the convolutional neural network used in the deep mind paper. The network consists of three convolutional layers with window sizes of 8x8,4x4, and 4x4 and a fully connected layers with 512 nodes along with and relu activation on all layers.Passing the state information through the neural network results in the networks estimation of the maximum future reward at the end of the game for each of the nine possible button commands (do nothing, left, right, up, down, jump, spin jump, jump right, spin jump right) from here forward these values will be referred to as Q-values. The system is given a small positive reward of +1 for increasing the game score, Which is achieved by killing enemies or collecting coins. A large positive reward of +100 is given for reaching the end of a level. A large negative reward of -100 is given to the system for dying and a small negative reward of -1 is given for any other action. Giving this constant negative reward will prevent the agent from remaining in one area and will ultimately prevent it from dying due to running out of time in a level. As per the DQN algorithm the next action performed is the one that has the highest Q-value or it is randomly selected. Allowing for random actions will let the agent more fully explore the possible options. The chosen action would then be performed on the emulator, after 50 frames of the action being repeated. The resulting state is stored along with the reward gained the actions effect, and whether the emulator has died or reached the end of the level.
To train the neural network a method called experience replay is used. Experience replay takes a random sample of the agents experiences which are defined by an array containing the following information:
1. Action taken
2. Original state
3. Resulting state
4. Reward
5. If Mario died or has completed the level
The Q-value of the original state is then updated by using the Bellman equation shown in figure 3 and back propagation. This equation updates the Q-value of an action performed at a given state this value is represented by the summation of the reward given to the agent for that action and the maximum discounted Q-value of the resulting state. This method of training will efficiently use the agents experiences by allowing the agent to train multiple times with any one experience.

This sequence of events is repeated until the agent has either reached the end of the level or died due to running out of time or hitting an enemy. In which case the emulator will reset the level. By replaying the level multiple times the program will gain a multitude of different experiences that are then used to train the neural network will be trained to find the optimal button selection that will allow Mario to reach the end of a level.
Expansion of this project
I have created a slightly modified agent to accommodate other 2D side scrolling video games namely the Atari games mentioned in the “Playing Atari with Deep Reinforcement Learning” paper. The modified agent uses the Atari games included in the AI gym reinforcement learning package which uses the games score to determine a reward. Outside of modifications to the reward system the rest of the algorithm remains the same. Currently the modified agent plays space invaders.
Link to the projects github repository
References
Mnih, V., Kavukcuoglu, K., Silver, D., Graves, A., Antonoglou, I., Wierstra, D., & Riedmiller, M. A. (2013). Playing Atari with Deep Reinforcement Learning. ArXiv Preprint ArXiv:1312.5602.
Mnih, V., Kavukcuoglu, K., Silver, D., Rusu, A. A., Veness, J., Bellemare, M. G., . . . Hassabis, D. (2015). Human-level control through deep reinforcement learning. Nature, 518(7540), 529-533. doi:10.1038/nature14236